Master Project Management Fundamentals Today
Project management fundamentals are the essential skills and frameworks you use to steer a project from a simple idea all the way to a successful launch. It’s all about expertly juggling key constraints—like scope, time, and budget—to hit your goals without a hitch.
What Are Project Management Fundamentals?
Let's be honest, the term 'project management' can sound a bit corporate and stuffy. But at its heart, it’s really just the organized practice of turning a vision into reality.
Think about building a house. You wouldn't just grab a hammer and some nails and hope for the best, right? You'd start with a clear vision, draft a detailed blueprint, line up all your materials and a skilled crew, and oversee the entire process until you’re finally handing over the keys.
That structured journey is project management. It gives you a roadmap to prevent chaos and keep everyone on the same page, pulling in the same direction. Getting these fundamentals down isn't about memorizing buzzwords; it's about building a strategic mindset that can guide any effort, big or small, to a successful conclusion.
The business world is taking notice, too. The global project portfolio management market is already valued at around $6.13 billion and is expected to keep growing. This trend shows just how much companies rely on structured management to connect their projects directly to their most important business objectives.
The Core Components of a Project
Every project is defined by a set of core components that project managers must constantly monitor and balance. Understanding these elements is the first step toward effective management.
The table below breaks down these essential pieces using our house-building example to make it concrete.
The Core Components of a Project
| Component | Description | Example (Building a House) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | The what—all the specific work and deliverables required to complete the project. | A 3-bedroom, 2-bathroom house with a two-car garage and a specific type of siding. |
| Time | The when—the project's schedule, including its start date, end date, and key milestones. | The 6-month timeline, with deadlines for foundation, framing, and interior finishing. |
| Cost | The how much—the total budget allocated for all resources, including labor, materials, and equipment. | The $300,000 budget covering all expenses from land purchase to final landscaping. |
| Quality | The how well—the standards and criteria the final product must meet. | Ensuring all construction meets local building codes and uses high-grade, durable materials. |
These components are interconnected, and a change in one almost always affects the others. This is where the real art of project management comes into play.
The Iron Triangle: A Constant Balancing Act
From launching a new software application to planning a major event, every single project operates under three universal constraints. This classic trio is famously known as the Iron Triangle:
-
Scope: This is the what of your project. It clearly defines the work that needs to get done and the precise features or results you're promising to deliver. For our house-building project, the scope would detail the number of bedrooms, the type of flooring, and the kitchen layout.
-
Time: This is your when. It represents the entire project schedule, from the official start date to the final deadline, including all the critical milestones in between. This is your timeline for laying the foundation, framing the structure, and finishing the interior work.
-
Cost: This is the how much. It covers the complete budget for the project, accounting for everything from labor and materials to permits and any other resources you'll need along the way.
A project manager's most critical job is to keep these three elements in balance. If a client suddenly decides they want to add a fourth bedroom (an increase in scope), you know it's going to demand more time and a bigger budget. Mastering this give-and-take is the absolute key to making any project a success.
Want to see how well you've grasped these core ideas? Test your knowledge with our project management fundamentals exam prep.
A Project's Journey Through 5 Key Stages
Every single project, whether you're rolling out a new software system or building a website, follows a natural lifecycle. It’s born from an idea, grows through careful planning and hard work, and finally reaches a conclusion. It doesn't just happen randomly.
To make sense of this, project managers often talk about the five process groups outlined by the Project Management Institute (PMI). Think of these not as rigid, sequential steps but as overlapping phases that guide a project from a simple concept to a finished product. Getting a handle on this flow turns a potentially chaotic undertaking into a structured, manageable process.
Initiating: The Project Gets Its Name
This is where it all starts. The Initiating phase is the official green light, the moment an idea becomes a real, recognized project. It’s not just a "what if" anymore; it's a formal endeavor with a clear reason for being. The main goal here is to define the project at a high level and get the official go-ahead to start committing resources.
So, what does that look like in practice?
- Developing a Project Charter: This is your project's birth certificate. It spells out the big-picture goals, names the key players (stakeholders), and, crucially, gives the project manager the authority to get things done.
- Identifying Stakeholders: You figure out everyone who has a stake in the project’s outcome. This includes your team, the executive sponsors, the people who will actually use the end product, and even outside vendors.
By the end of this phase, there should be no question about what the project is and why it matters.
Planning: Drawing Up the Blueprints
Once you have the green light, you enter the Planning phase. If initiation was the spark of inspiration, planning is where you meticulously draw up the architectural blueprints. I can't stress this enough: this is the most critical stage. The quality of your planning has a direct and massive impact on your project's success. As the old saying goes, failing to plan is planning to fail.
This is where you build the detailed roadmap your team will follow. You're defining the how, what, when, and who of the entire project, leaving as little to chance as possible.
The image below really captures a core part of this: nailing down the project's scope.
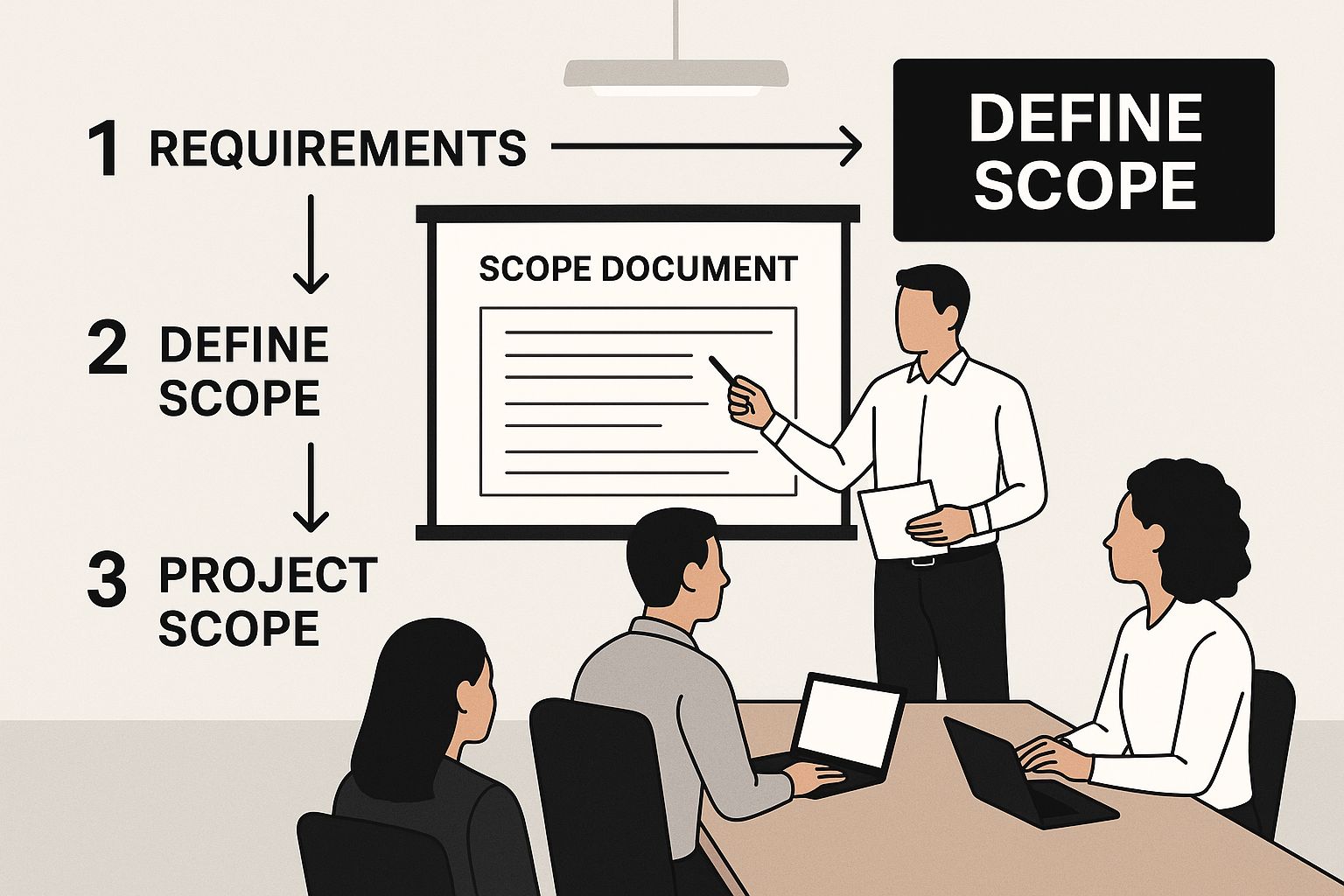 Image
Image
As the graphic shows, getting crystal clear on what is—and just as importantly, what is not—part of the project is fundamental. It's your best defense against scope creep down the line.
Executing: Breaking Ground and Building
With a solid plan in your hands, it’s time to get to work. The Executing phase is where the magic happens. This is where the team rolls up their sleeves and starts building, coding, installing, and creating the deliverables you defined in the plan. Naturally, this is also where most of the project's budget gets spent.
The project manager's job shifts here from an architect to a conductor. You're now orchestrating the team, juggling resources, and making sure the work gets done on schedule. Constant, clear communication is the fuel that keeps the engine running smoothly.
Monitoring and Controlling: The Foreman's Watchful Eye
Now, this next phase—Monitoring & Controlling—doesn't just happen after executing. It happens at the same time. Picture a construction foreman constantly walking the site, comparing the work in progress to the blueprints. That's this phase in a nutshell.
This stage is all about keeping your finger on the pulse of the project. You're tracking progress against your plan, measuring performance, and spotting any deviations before they become disasters. If things start to go sideways, this is when you step in to make corrections and get back on track.
This continuous oversight is what separates a well-run project from a chaotic one. It's interesting to note that while only about 23% of organizations report using project management software, a whopping 77% of high-performing projects rely on these tools to track their progress. If you're curious, you can dig into more industry statistics about project management software and its impact.
Closing: The Keys are Handed Over
All good things must come to an end. The Closing phase is the formal wrap-up of the entire project. It’s not just about stopping work; it's about a clean, official handover that ties up all the loose ends.
Here’s what a proper closing looks like:
- Deliver the final product: You formally present the finished work to the client or stakeholders.
- Archive project documents: All the plans, reports, contracts, and lessons learned are filed away for future reference. This is a goldmine for the next project.
- Release the project team: The team is officially disbanded, freeing them up for new assignments.
- Celebrate success: Take a moment to recognize the hard work and toast to a job well done!
Closing a project properly isn't just an administrative task. It ensures a smooth transition and captures invaluable knowledge, setting your organization up for even greater success next time.
Choosing the Right Project Methodology
Think of a project manager like a master chef. A great chef doesn't use the same recipe for every single dish—they have a whole cookbook to choose from. In the same way, a savvy project manager needs more than one way to get a project across the finish line.
A project methodology is your "recipe for success." It’s a formal set of principles and practices that guides your project from start to finish. If you try to use the same methodology for every project, you're bound to run into trouble. It's like trying to bake a cake using instructions for grilling a steak; the results will be a complete mess.
To really succeed, you need to understand the core differences between the major methodologies. The two you'll run into most often are Waterfall and Agile. Each offers a totally different path to success, and picking the right one can be the deciding factor between a smooth delivery and a project that’s a constant struggle.
Let's break them down.
The Classic Waterfall Approach
The Waterfall methodology is the old-school, traditional way of managing projects. Its name is the perfect metaphor for how it works: progress flows steadily downwards in one direction, like a waterfall. You work through a series of distinct phases, and you absolutely must finish one before the next one can begin. No exceptions.
Imagine building a house. You can't start putting up the walls until the foundation is poured and fully cured. You can’t hang drywall before the electrical and plumbing are run. That logical, step-by-step process is the very heart of the Waterfall method.
This approach is all about predictability and tight control. It really shines when:
- Requirements are set in stone: The project's goals and deliverables are perfectly clear from day one and aren't expected to change.
- The environment is stable: There are very few unknowns or potential surprises that could throw the plan off course.
- Documentation is critical: A heavy emphasis is placed on detailed documentation at every stage, creating an unmistakable paper trail of all decisions and progress.
Because of this rigid structure, Waterfall is a fantastic choice for projects like construction, manufacturing, or government work where following the original plan to the letter is a must.
The Flexible Agile Framework
On the other hand, Agile is less of a rigid recipe and more like a creative chef testing and tasting a new dish as they cook. It’s a modern approach built for speed, flexibility, and customer collaboration, especially in fast-paced industries like software development.
Instead of one long, linear process, Agile breaks the project into small, bite-sized cycles called sprints.
Each sprint, which usually lasts between one and four weeks, acts like a mini-project. The team works to design, build, and test a small, functional piece of the final product. At the end of every sprint, they get feedback from stakeholders and use those insights to adjust the plan for the next cycle. This cook-taste-adjust loop allows for constant improvement and helps ensure the final product is what users actually need, even if those needs change along the way.
Agile is built on the idea that change is not just possible, but inevitable. It's something to be embraced, not fought against. The focus is on collaborating with the customer and responding to change rather than just blindly following a plan.
This makes Agile the perfect fit for projects where the requirements aren't fully known at the start or are likely to shift. It’s the go-to for software development, creating marketing campaigns with a tool like Asana, and R&D projects where learning and adapting are the whole point.
A Head-to-Head Comparison
To make the differences crystal clear, let's put these two methodologies side-by-side. Seeing their core traits compared directly can help you quickly figure out which approach best fits your project's specific needs and constraints.
Here’s a quick rundown of how they stack up.
Waterfall vs Agile: A Quick Comparison
| Characteristic | Waterfall | Agile |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Linear and sequential; one phase must finish before the next begins. | Iterative and incremental; work is done in short cycles (sprints). |
| Flexibility | Rigid; changes are difficult and costly to implement once a phase is complete. | Highly flexible; changes are welcomed and can be incorporated in future sprints. |
| Planning | All planning is done upfront before any execution starts. | Planning is continuous; a high-level plan is set, but details are planned each sprint. |
| Customer Involvement | Limited to the initial requirements phase and the final delivery. | High; constant feedback and collaboration are integral to the process. |
| Best For | Projects with fixed requirements and a stable environment (e.g., construction). | Projects with evolving requirements and a dynamic environment (e.g., software). |
At the end of the day, the question isn't "Which methodology is better?" but rather, "Which one is better for this specific project?" By getting a solid handle on these project management fundamentals, you can properly analyze your project's goals and environment to make the right call—setting your team up for success right from the start.
Mastering the Ten Knowledge Areas
If the five process groups are the road a project travels, then the ten knowledge areas are the specific skills you need to navigate that road. Think of them as your project management toolkit—the core competencies you need to master. Rather than just rattling them off in a long list, it’s much more practical to group them by what they actually do.
We can break them down into three intuitive categories: the Core Planners, the Execution Enablers, and the Strategic Guardians. Getting a handle on these is fundamental to your success as a project manager. Let's dig into what each one looks like on a real project.
 Image
Image
The Core Planners
This first set of four knowledge areas is the absolute bedrock of any project plan. They’re all about defining what you're actually building, how long it's going to take, and what resources you'll need. Getting these right from the start is non-negotiable.
1. Integration Management This is the big one—the conductor of the orchestra. Integration Management is all about making sure every part of the project works together in harmony. It’s the master process that weaves the other nine knowledge areas into a single, cohesive strategy.
- Practical Example: You're building a new mobile app and the client decides they need a new login feature. Integration management is how you assess that change and update the schedule, budget, and resource plan accordingly, making sure the whole team is aligned on the new direction.
2. Scope Management This is where you draw the lines. Scope Management is focused on defining exactly what work is included in the project and, just as crucially, what isn't. A well-defined scope is your best defense against "scope creep"—that dreaded, gradual expansion of a project beyond its original goals.
3. Schedule Management Once you know what you're building, you need to figure out when it’ll be ready. This area involves creating a realistic project timeline, putting tasks in the right order, and setting firm deadlines for key milestones. A good schedule is the engine that keeps your project moving forward.
- Practical Example: You use a Gantt chart to map out a new marketing campaign launch. It clearly shows that the ad copy has to be written before the graphic designer can start their work, creating a logical flow and preventing bottlenecks.
4. Cost Management This is where you put on your accountant hat. Cost Management covers everything related to the project's finances. It involves estimating the costs for all your resources—people, materials, software—and then creating a formal budget and tracking spending to make sure you don't go over.
The Execution Enablers
With a solid plan locked in, this next group is all about the "doing." These knowledge areas focus on the people and processes needed to bring your plan to life. They are the day-to-day skills that empower your team to do their best work.
5. Quality Management This isn't about running a final spell-check. It’s about embedding quality into the entire process from day one. Quality Management is where you define the standards your project must meet and implement checks and balances to ensure the final product is truly fit for purpose.
A common pitfall is to treat quality as just a final inspection. True Quality Management is proactive. It’s about designing processes to prevent defects, not just catch them before they get to the customer.
6. Resource Management Projects don't happen without people and tools. This is the art of getting the right team together and making sure they have everything they need to succeed. It covers acquiring, managing, and developing your team, as well as securing any physical resources like equipment or software.
- Practical Example: For a website redesign, you identify the need for a front-end developer, a UX designer, and a copywriter. You then book their time, get them the software licenses they need, and set up a workflow for their collaboration.
7. Communications Management Clear, consistent communication is the lifeblood of a healthy project. This knowledge area is about creating a deliberate plan for who gets what information, when they get it, and how. It ensures every stakeholder, from the CEO to the junior developer, is kept in the loop.
The Strategic Guardians
This final trio of knowledge areas serves as your project's early warning and defense system. They are focused on looking ahead and around, protecting your project from nasty surprises while keeping it aligned with the bigger business picture.
8. Risk Management Let's be real: things go wrong. Risk Management is the process of looking into the future to identify potential problems that could derail your project. You then analyze how likely they are to happen and what the damage would be, and develop plans to handle them if they do.
9. Procurement Management Sometimes you need to bring in outside help. Procurement Management is how you handle relationships with vendors, contractors, and suppliers. This includes everything from writing contracts and choosing the right partner to overseeing their work and formally closing out the agreement.
- Practical Example: Your software project requires a specialized cloud database service. You research providers, request proposals, negotiate a contract with the best vendor, and then manage that partnership throughout the project.
10. Stakeholder Management Last but not least, this is all about the people. Stakeholder Management involves identifying everyone who has a vested interest in your project and developing strategies to keep them engaged and on your side. This means understanding their expectations, addressing their concerns, and communicating effectively to maintain their support. To really cement these concepts, going through an IT certification exam prep course can be invaluable, as they cover these critical areas in detail.
Finding Your Project Management Command Center
Let's be honest: modern projects just can't run on spreadsheets and endless email chains anymore. If you want to keep up, your team needs a central hub—a "command center"—to organize work, see what’s happening, and actually talk to each other effectively. This is where project management software stops being a "nice-to-have" and becomes a fundamental part of your toolkit.
These platforms aren't just glorified to-do lists; they're the digital backbone that holds a successful project together. They bring much-needed clarity to complex workflows, heading off the kind_of communication breakdowns and missed deadlines that can sink a project before it even gets going. There's a reason this market is booming. Projections show it hitting $7.24 billion by 2025 and rocketing to $12.02 billion by 2030. You can dig into more of the data on these adoption trends on monday.com. That explosive growth tells a story: these tools are becoming non-negotiable for getting things done.
Types of Project Management Tools
Not all software is built the same. Different tools are designed to solve different kinds of problems, and they usually fall into a few main categories. Figuring out these types is the first step to finding the right fit for your team.
-
Visual Task Managers: Think of tools like Trello or Asana. They are brilliant for more straightforward projects. They often use Kanban boards to lay out the workflow visually, so at a glance, everyone can see what’s being worked on, what's coming up next, and who owns each piece.
-
Comprehensive Platforms: When you're dealing with more intricate projects—especially in areas like software development or engineering—you need more firepower. Platforms like Jira or monday.com are essential here. They pack in advanced features for detailed planning, resource allocation, bug tracking, and deep-dive reporting.
-
Communication Hubs: Sometimes, the biggest hurdle is just keeping everyone in sync. Tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams act as the project's central nervous system. They pull in notifications and conversations from other software, keeping everything organized and—most importantly—out of your cluttered email inbox.
Take a look at this screenshot from monday.com. It’s a perfect example of how a comprehensive platform can pull tasks, timelines, and ownership into one clear picture.
An integrated dashboard like this is so powerful because it gives you instant visibility into the health of your project. Nothing important gets lost or falls through the cracks.
Choosing the Right Software
Here’s the simple truth: the best tool is the one your team will actually use. Your choice has to match your team’s real-world workflow and the project management methodology you've committed to, whether it's Agile, Waterfall, or something in between.
When you’re looking at software, focus on the specific problem you're trying to solve. Are missed deadlines your biggest headache? Look for a tool with strong timeline and notification features. Is a lack of visibility causing chaos? Prioritize platforms with great dashboards and reporting.
It’s easy to get distracted by a long list of shiny features you'll never touch. Instead, ground your decision by asking these questions:
- What is our biggest pain point right now? (Is it communication, task tracking, or resource planning?)
- Does this tool actually fit our project methodology? (For example, Kanban boards for Agile or Gantt charts for Waterfall.)
- Honestly, is it easy for my team to learn and use? (A steep learning curve can kill adoption.)
- Does it play nice with the other tools we already depend on?
Answering these questions gives you a simple, practical way to pick a command center that doesn't just become another monthly subscription, but one that genuinely makes your projects run smoother.
From Theory to Reality: Making Project Management Best Practices Work for You
 Image
Image
It’s one thing to know the textbook definitions of project management, but it's another thing entirely to put them into practice day in and day out. Consistently applying best practices is what truly separates the projects that succeed from those that just limp across the finish line. Think of them as the habits that turn project management fundamentals from abstract ideas into a reliable toolkit for getting things done.
The whole journey kicks off with one simple, yet critical, step: defining crystal-clear goals. Without a shared, concrete understanding of what "done" actually means, your team is essentially flying blind. Imagine your team building a new app feature. The developers are focused on making it blazing fast, but the stakeholders are actually most concerned with ironclad security. That kind of disconnect is a recipe for rework, wasted money, and a whole lot of frustration.
Build a Culture of Open Communication
Clear, honest communication is the lifeblood of any project. This goes way beyond just sending out a weekly status report. It's about creating a safe environment where information flows freely in all directions—up, down, and sideways. Teams that nail this can tackle problems faster and handle unexpected changes with far less chaos.
Here's a classic example: A project hits a nasty technical bug. The developer, afraid of getting blamed, keeps it to themself. By the time the project manager discovers the issue, the timeline has slipped by a full week. In a team with open communication, that same developer would have flagged the problem immediately, allowing the team to swarm it and find a fix in hours, not days.
This kind of open dialogue is the foundation of trust and keeps everyone rowing in the same direction.
Stay Ahead of Risks and Keep Stakeholders Close
The best project managers I've ever worked with are always thinking two steps ahead. They don't just sit back and wait for fires to start; they actively hunt for potential risks before they have a chance to derail the project. This proactive approach is a total game-changer.
Just as crucial is keeping your stakeholders engaged from start to finish. They aren't just names on a report; they're your partners. Keeping them in the loop and genuinely involving them builds incredible buy-in and can turn a potential critic into your biggest advocate. A project's ultimate success often comes down to how well you manage these human dynamics. For anyone studying for certification exams, mastering these concepts is non-negotiable. You can sharpen these skills with our IT and project management certification exam preparation resources.
A simple gut-check can help keep these practices top of mind:
- Clearly Defined Goals: Do we have a written, agreed-upon definition of what a "win" looks like for this project?
- Transparent Communication: Does every single person on the team feel safe enough to raise a red flag or admit a mistake?
- Active Risk Management: Are we regularly asking, "What could go wrong?" and planning for it?
- Consistent Stakeholder Engagement: Am I talking to key stakeholders regularly, not just when I have bad news to share?
Frequently Asked Questions in Project Management
As you get your hands dirty in the world of project management, you'll find that a few key questions always seem to pop up. Let's tackle some of the most common ones I hear, whether you're just dipping your toes in or you're a seasoned pro looking to refine your approach.
What Is the Most Important Skill for a Project Manager?
If I had to pick just one, it would be communication. Hands down. While knowing the technical side of things is a huge plus, a project manager is ultimately the central hub for all information.
Think of it this way: you're constantly connecting the dots between stakeholders, your own team members, clients, and outside vendors. Your ability to set clear goals, give useful feedback, and keep everyone's expectations in check is what holds the entire project together.
When a project goes off the rails, poor communication is almost always a prime suspect. It's the root cause of misaligned teams, missed requirements, and tanking morale, making it a leading reason why projects fail.
Can I Manage a Project Without a Formal Certification?
Yes, you absolutely can. Certifications like the PMP (Project Management Professional) are fantastic for providing a solid framework and definitely add weight to your resume. But the true heart of project management is putting fundamental principles into action every single day.
I've worked with many incredible project managers who have no formal credentials. They succeed because they have killer organizational skills, natural leadership, and—you guessed it—excellent communication. You can absolutely master the craft through hands-on experience, self-study, and by using great project management software. Certification often becomes more crucial when you want to lead massive, complex projects or climb the ladder in certain corporate environments.
How Do I Choose Between Agile and Waterfall?
This is a classic question, and the answer really boils down to one thing: predictability. The right methodology depends entirely on the nature of your project.
-
Go with Waterfall if your project requirements are rock-solid, fully documented, and unlikely to budge. It's perfect for industries like construction or manufacturing, where you need a predictable, step-by-step process to maintain control.
-
Opt for Agile when you expect requirements to change or when you don't know all the details upfront. This is the daily reality in software development and R&D. Agile's iterative approach gives you the flexibility to adapt, get feedback quickly, and continuously improve, making sure the final product is what users actually need now.
Ready to test your knowledge and get certified? HydraNode offers an AI-powered exam prep platform to help you master these concepts and pass your IT certification exams with confidence. Explore our adaptive practice tests at https://www.hydranode.ai.



