Ultimate Guide to Migration to Cloud Computing for Your Business
Moving to the cloud isn't just a technical swap-out. It’s a strategic business move. You're shifting your company's core digital operations—from applications and databases to your entire IT infrastructure—from on-site servers to a cloud environment. Getting this right means more than just a successful IT project; it's about fundamentally improving how your business scales, manages costs, and performs.
Your Cloud Migration Journey Starts Here
Embarking on a cloud migration is a major undertaking for any company. I've seen firsthand that it's far more than trading physical servers for virtual ones. This is a strategic realignment that touches everything from your operational agility to your financial forecasting. When done right, it opens up incredible opportunities for innovation. But success depends entirely on a solid, well-defined roadmap that connects every technical step back to a clear business objective.
A methodical approach is your best defense against common headaches like budget blowouts and unexpected downtime.
The sheer scale of this shift is hard to overstate. The global cloud computing market is on track to hit $1.614 trillion by 2030. That’s not just a number; it’s a massive signal that businesses everywhere are leaving traditional IT behind. This explosive growth is fueled by the demand for flexible, data-centric technologies that can power everything from remote workforces to advanced AI. For more on these trends, you can find some great cloud computing insights on N2WS.com.
Mapping Out the Four Core Phases of Cloud Migration
A successful cloud migration isn’t a single leap; it’s a journey broken down into distinct, manageable phases. I've guided dozens of companies through this process, and it always comes down to these four critical stages: assessment, planning, execution, and post-migration optimization. Each one builds on the last, and skipping or rushing any of them is a recipe for trouble.
Think of it like building a house. You wouldn't start pouring a foundation without a blueprint, and you wouldn't move in before the plumbing and electricity were checked. The same logic applies here.
This table provides a high-level overview of what each phase entails.
| Phase | Key Objective | Primary Activities |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Assess & Discover | Understand your current environment and define business goals. | Inventory applications, map dependencies, analyze performance metrics, and establish clear success criteria. |
| 2. Plan & Design | Create a detailed migration strategy and technical blueprint. | Choose a cloud provider, select migration strategies (e.g., rehost, refactor), design the target architecture, and create a timeline. |
| 3. Execute & Migrate | Move the workloads to the new cloud environment. | Provision cloud infrastructure, migrate applications and data, and perform initial testing in a controlled manner. |
| 4. Validate & Optimize | Ensure everything works as expected and continuously improve. | Conduct performance and security validation, optimize costs, and fine-tune resources for maximum efficiency. |
Seeing the journey laid out this way helps clarify that migration is a structured process, not a chaotic scramble. Each step is designed to minimize risk and maximize the eventual return on your investment.
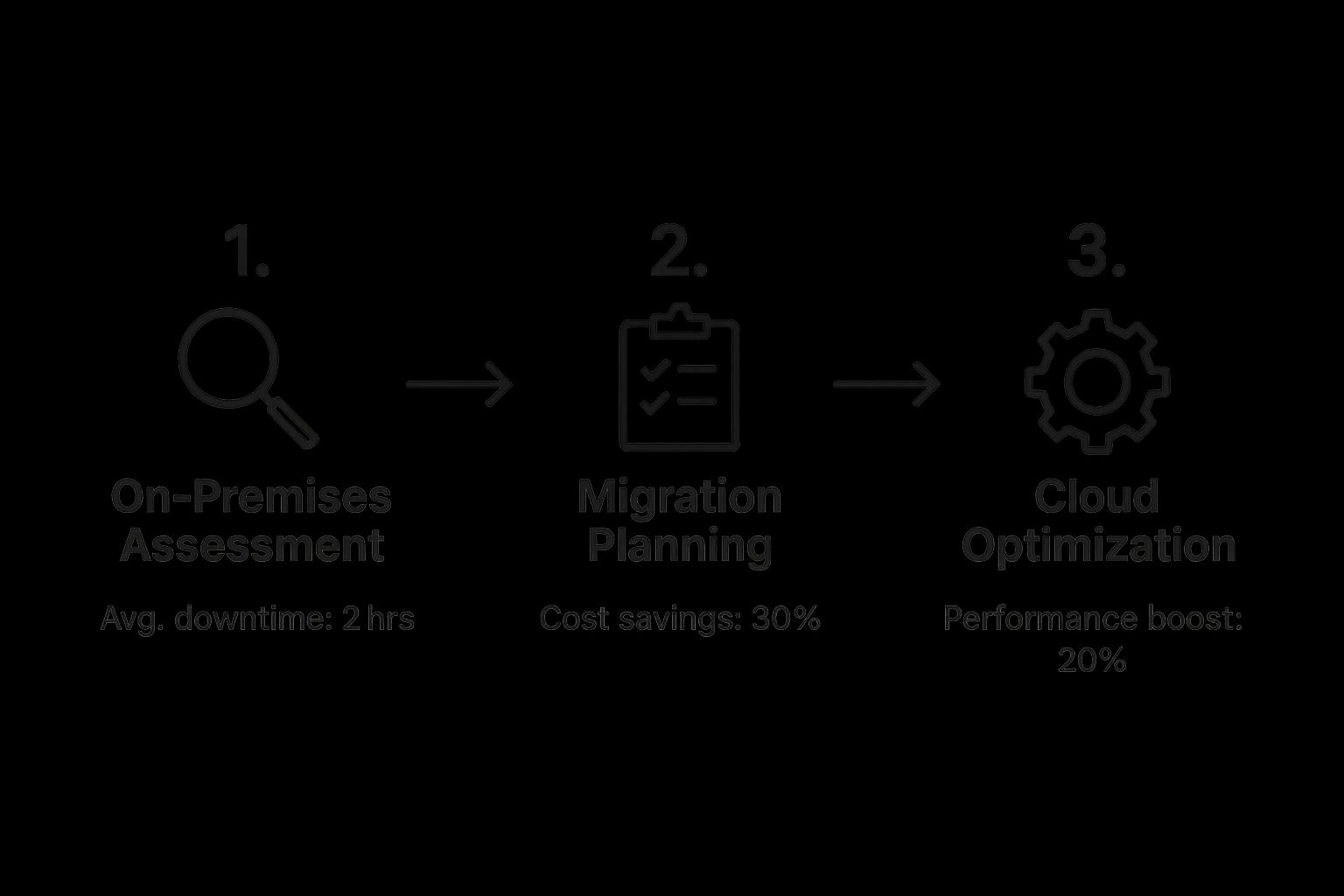
This infographic helps visualize how a structured migration leads to tangible business benefits.
 Image
Image
As you can see, a well-managed project can deliver real results: less downtime, significant cost savings, and a big boost in application performance. These outcomes don't happen by accident; they're the product of a meticulous, phase-by-phase plan.
The most common mistake I see is teams treating cloud migration as a pure IT project. The truly successful migrations are viewed as business initiatives from day one. Every technical decision must be tied to a commercial goal, whether that’s getting products to market faster or creating a better customer experience.
Ensuring your team is ready for this new environment is crucial. Managing a modern cloud stack requires new skills. You might want to look into how your team can get certified, and intelligent tools can make a big difference. Exploring a platform like the AI-powered exam preparation from Hydranode can help get your staff up to speed quickly.
In the next sections, we'll dive deep into each of these phases, giving you the practical, step-by-step guidance you need to navigate your cloud migration with confidence.
Building Your Pre-Migration Assessment
 Image
Image
Any successful cloud migration starts with a rock-solid foundation, and that foundation is the pre-migration assessment. This isn't just about ticking off items on a generic checklist. It's a deep-dive investigation into your entire IT landscape to prevent those nasty, expensive surprises later on. Honestly, skipping this step is one of the top reasons I've seen migrations stumble or blow their budgets.
Think of it like getting an architectural survey before a major home renovation. You absolutely need to know where the load-bearing walls are and what's going on with the plumbing before you even think about picking up a sledgehammer. This assessment is your blueprint.
Cataloging Your IT Portfolio
The first order of business is creating a complete inventory of every single application, server, and database in your current setup. And I don't mean just a list of names. You need to dig in and capture the nitty-gritty details from your configuration management database (CMDB), along with performance metrics and what it actually costs to run each asset.
I was once brought in to help a retail company whose migration almost went completely off the rails. Why? They missed a small, legacy inventory management tool. It wasn't officially on the books but was absolutely essential for two of their regional warehouses. Finding this during the assessment saved them from what would have been a catastrophic operational failure.
To build out your inventory, focus on these key areas:
- Applications: Document every piece of software. This includes everything from your massive enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems down to the small, specialized utilities used by a single department.
- Infrastructure: Get a full count of all physical and virtual servers. Make sure to note their specs, like CPU, RAM, and storage configurations.
- Databases: List out every database, its size, the type (like SQL or NoSQL), and its specific performance needs.
Uncovering Hidden Dependencies
Once your inventory is in place, the real detective work begins: mapping dependencies. Applications rarely live in a vacuum. They talk to other apps, pull data from specific databases, and rely on a web of network services. A migration to cloud computing that ignores these intricate connections is, frankly, doomed from the start.
This is where automated discovery tools are worth their weight in gold. They can scan your network and create a visual map of how everything interacts, often uncovering forgotten connections and "shadow IT" that even your best engineers didn't know about.
A thorough dependency map is your single most valuable asset in migration planning. It directly informs which applications must move together, dictates the migration sequence, and prevents the dreaded "we moved it, and now something else broke" scenario.
Take an e-commerce platform, for example. On the surface, it might look like a single unit. But dig a little deeper, and you’ll find it connects to a separate payment gateway, a third-party shipping calculator, a customer relationship management (CRM) system, and an analytics database. Trying to move just the main app without its partners would be an absolute disaster.
Analyzing Workloads and Performance
With a clear map of your assets and how they're all connected, you can start analyzing their performance and how critical they are to the business. Not all workloads are created equal. This analysis is crucial for prioritizing what moves first and, more importantly, how it moves.
Start by gathering performance data over a meaningful timeframe, like a full business quarter, to see the natural peaks and valleys in usage. You'll want to look at metrics such as:
- CPU and Memory Utilization: This tells you which apps are resource hogs and could really benefit from the cloud's ability to scale on demand.
- I/O Operations per Second (IOPS): This is absolutely critical for database performance and will directly influence your cloud storage choices.
- Network Bandwidth: Understanding your data transfer patterns is key for managing both performance and your monthly cloud bill.
This data-driven approach shifts the conversation from guesswork to objective reality. A workload that seems simple might have complex security or data sovereignty rules attached, making it a poor choice for an early move. On the other hand, a resource-hungry but non-critical app could be the perfect "quick win" to build momentum and validate your migration process. This assessment is what builds the business case for your entire migration to cloud computing project.
Crafting Your Cloud Migration Strategy
 Image
Image
With a solid assessment in your back pocket, you have the blueprint. Now it's time to put on your architect's hat and design a cloud migration strategy that actually works. This isn't about just picking a popular cloud provider and hoping for the best. It's about deliberately choosing how each piece of your IT puzzle will find its new home in the cloud.
This is the phase where ambition meets practicality. A well-thought-out strategy directly connects your technical decisions to your business goals. It sets the stage for a smoother execution and, more importantly, ensures you actually get the benefits you're after. Think of it as the bridge between knowing what you have and getting where you want to go.
Understanding the 7 Rs of Migration
The "7 Rs" are a fantastic framework that I've seen work time and time again. It helps you categorize your applications and decide on the smartest migration path for each one. Don't think of it as a rigid set of rules, but more like a menu of options. Instead of forcing a one-size-fits-all approach, you can tailor your strategy to what each specific workload needs, optimizing for cost, performance, and effort.
-
Rehost (Lift and Shift): This is your most straightforward move. You take an application and drop it onto cloud infrastructure with minimal, if any, changes. It’s fast and perfect for legacy systems you can't really touch or for scoring some quick wins. Moving a simple file server directly to a cloud VM is a classic example of rehosting.
-
Replatform (Lift and Tweak): Here, you make a few smart, cloud-specific optimizations without overhauling the core application. Imagine moving your on-premises database to a managed service like Amazon RDS. You're not rewriting the app, but you're instantly gaining benefits like automated backups and patching.
-
Refactor (Re-architect): This is the most intensive option, but often the most rewarding. You're redesigning an application to be fully cloud-native. This is the path for your strategic, high-value apps where you want to squeeze out every bit of scalability and resilience. Breaking down a clunky, monolithic e-commerce app into nimble microservices is a prime example of refactoring.
-
Repurchase: Let's be honest—sometimes it's just easier to switch to a different product. This usually means moving from a self-hosted tool to a modern SaaS solution. A common scenario is finally ditching that old, on-prem CRM system for a subscription to a cloud-based powerhouse like Salesforce.
The other three "Rs" are just as important because they focus on what you'll leave behind:
-
Retire: Your initial assessment probably dug up some skeletons—applications that are no longer used or are completely redundant. Shutting them down is the easiest way to cut costs and reduce complexity.
-
Retain: Some applications might need to stay on-premises for now. This could be for heavy regulatory reasons, compliance mandates, or latency issues. A factory control system that needs near-instant response times is a great candidate for retention.
-
Relocate: This is a more specialized approach, typically involving moving infrastructure between data centers without changing the applications themselves. It’s a common tactic in hybrid cloud scenarios.
Choosing Your Cloud Provider and Building the Plan
Picking a cloud provider like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP) has to be about more than just marketing hype. Base your decision on practical, real-world factors. Does your team already have deep expertise in Azure? That's a huge point in its favor. Is your most critical application built on technology that integrates beautifully with GCP? That could be your deciding factor. Dig into their cost structures, regional availability, and the specific services that truly match your workload requirements.
You'll notice a growing trend toward multi-cloud and hybrid environments, and it’s for good reason. Today, a staggering 89% of organizations have a multi-cloud strategy, mixing services to get the best of all worlds. While this approach adds some complexity, the payoff can be huge, with companies often cutting IT management costs by 20% to 30%. You can dig deeper into these deployment models and their financial impact by reviewing the latest cloud migration statistics on duplocloud.com.
Once you've assigned an "R" to each application and selected your provider(s), you can build your project plan. This plan needs to be detailed and brutally realistic. It must include:
- Timelines: Break the migration into manageable phases. I always recommend starting with low-risk applications to score early wins and build team confidence.
- Budgets: Don't forget to account for everything—direct cloud costs, migration tools, and potential staff training or outside help.
- KPIs: You have to define what success looks like. Will you measure it by reduced server provisioning time, lower operational costs, or improved application uptime? Be specific.
A phased rollout is your best friend. I once worked with a financial services firm that started their migration by moving an internal reporting tool. It was low-risk but highly visible. The project's success generated huge internal buy-in and provided invaluable lessons that we applied when we later migrated their core trading platform.
This level of detailed planning requires a team with a clear vision and a deep understanding of the tech involved. Learning more about the philosophy and expertise behind a company like HydraNode can offer great insight into how seasoned teams tackle these kinds of complex challenges. Ultimately, a successful migration to cloud computing is a story of great strategy and even better execution.
Executing Your Migration and Ensuring Success
This is where the rubber meets the road. All your planning and assessments have led to this moment: the execution phase. It’s time to take those blueprints and build your new home in the cloud. Honestly, this is the most exciting part, but it’s also where precision and a steady hand are absolutely critical to make sure the new environment doesn't just work, but shines.
https://www.youtube.com/embed/N_U-5uIVc6o
The first real step is to build out the foundational infrastructure. Forget just spinning up virtual machines; this is about methodically constructing a secure, high-performance network. You'll start by carving out your slice of the cloud with a virtual private cloud (VPC) or virtual network (VNet), then defining subnets, routing tables, and internet gateways. Think of this as laying the digital plumbing and electrical for your new house.
Once the network backbone is in place, security becomes the immediate priority. You’ll implement security groups and network access control lists (NACLs), which act as your primary firewalls. These rules control every bit of traffic flowing in and out of your instances, forming the first line of defense for your cloud assets.
Establishing Robust Access Control
A secure cloud is built on a simple but powerful principle: least privilege. Your most important tool for enforcing this is Identity and Access Management (IAM). The goal is to create IAM roles, groups, and policies that grant users and services the exact permissions they need to do their jobs—and not a single permission more.
It’s tempting to assign broad, overly permissive roles to save time, but don't do it. I once worked with a client whose initial IAM setup gave nearly every developer "administrator" access. It was simple, sure, but it was also a massive security hole waiting to be exploited. We spent a full week carefully re-crafting their policies to grant specific, granular permissions—like "read-only access to specific S3 buckets" or "permission to restart certain EC2 instances"—which dramatically lowered their risk profile.
A smart IAM strategy always includes:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Don’t assign permissions to individual users. Instead, create roles based on job functions (e.g., "DatabaseAdmin," "WebAppDeveloper") and assign permissions to those roles.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Make MFA mandatory for all users, especially privileged ones. This one step can prevent 99.9% of account compromise attacks. It’s a non-negotiable.
- Regular Audits: Routinely review who has access to what. People change roles, and projects end. Cleaning out old, unnecessary permissions is basic security hygiene.
Moving Your Data and Applications
With a secure environment ready to go, you can finally start moving your workloads. The specific tools and methods you'll use depend entirely on which "R" strategy you chose—rehost, replatform, or refactor. No matter the approach, minimizing downtime is the name of the game.
For a classic "lift and shift" rehost, tools like AWS Application Migration Service (MGN) or Azure Migrate are lifesavers. They replicate your servers to the cloud in the background, keeping everything in sync until you're ready for the final, quick cutover. I've personally seen these tools shrink a planned weekend-long downtime into a tight, two-hour window.
When it comes to moving huge amounts of data, you can't fight physics. Trying to upload terabytes over a standard internet connection can literally take weeks. That's where physical transfer devices like AWS Snowball or Azure Data Box are invaluable. They ship you a secure appliance, you load your data on-site, and then ship it directly to a cloud data center for a high-speed upload.
Key Takeaway: Always, always perform a pilot migration. Before you even think about touching a critical production system, move a less important but representative application first. This is your dress rehearsal. It will expose any hidden issues with your network configuration, security policies, or migration tools in a low-stakes setting.
Validating Performance and Security
Just because your data is sitting in the cloud doesn't mean the job is done. Now comes the crucial validation step, where you prove that everything is working as it should—or even better than before.
Kick things off with performance testing. Use load testing tools to hammer your applications with simulated peak traffic. Does everything stay responsive? Does it scale correctly? Compare the results against the performance benchmarks you took before the migration. It’s very common to have to "right-size" some instances at this stage, tweaking CPU and RAM to hit that sweet spot between performance and cost.
Next, it's time for a thorough security audit. Run vulnerability scans and penetration tests against your new cloud environment. You're looking for misconfigurations or weaknesses that might have crept in. Cloud providers offer great tools for this, like Amazon Inspector or Microsoft Defender for Cloud, which can automate checks against security best practices.
Finally, bring in your users for User Acceptance Testing (UAT). Their feedback is the ultimate measure of success. They will immediately spot usability quirks or workflow problems that no automated test can catch. A migration to cloud computing is only truly complete when the people using the applications are happy, productive, and see the benefits.
Optimizing Your Cloud Environment After Migration
 Image
Image
Here's a hard truth many companies learn too late: the biggest mistake you can make is thinking your migration to cloud computing is over the moment the last server goes live. In reality, you've just reached the starting line. The real power of the cloud isn't just being there; it's treating it as a dynamic environment that needs constant care and attention.
Your focus now shifts from the project of migration to the practice of optimization. This is where you'll transform your new environment from a simple replica of your on-premise setup into a finely tuned, cost-effective engine that drives your business forward. It all comes down to a new way of thinking, centered on continuous improvement across cost, performance, and governance.
Embracing FinOps for Cost Control
One of the first reality checks after moving to the cloud is managing the monthly bill. The pay-as-you-go model offers incredible flexibility, but it's a double-edged sword that can lead to some shocking invoices if you aren't paying attention. This is precisely why adopting a FinOps (Financial Operations) culture is so critical.
FinOps isn't just a fancy term for cutting costs. It’s about building a framework for making smart, data-backed spending decisions. The very first thing to do is get a crystal-clear picture of where every dollar is going. Use your provider's built-in tools, like AWS Cost Explorer or Azure Cost Management, to tag your resources meticulously. This lets you slice and dice your spending by project, team, or application.
Once you have that visibility, you can start hunting for real savings:
- Zap Zombie Resources: Look for virtual machines running 24/7 that are only needed during business hours. A simple automation script can shut them down at night and on weekends, instantly saving you money.
- Cut Out Orphaned Storage: It's incredibly common to find unattached storage volumes left behind after a virtual machine was terminated. These "orphan" resources quietly rack up charges every month.
- Set Up Budget Alarms: Don't wait for the end-of-month bill shock. Proactively set alerts that fire off a notification when spending for a service or project is on track to blow past its budget.
Tuning Performance for Peak Efficiency
Cost and performance are two sides of the same coin. An oversized, sluggish virtual machine isn't just performing poorly—it's also wasting your money. The goal is to "right-size" your infrastructure. You want to give every single workload exactly the resources it needs to do its job well, without any expensive excess.
Start by digging into the performance metrics of your most important applications. Every major cloud provider gives you detailed monitoring tools that show CPU utilization, memory consumption, and I/O patterns. If you spot a server that consistently cruises along at 20% CPU usage, it's a perfect candidate for downsizing to a smaller, cheaper instance.
Pro Tip: Don't get fooled by averages. You have to analyze peak usage. A server might look over-provisioned on average, but if it spikes to 95% CPU during a critical report run, downsizing could cripple your business operations. True right-sizing is a balancing act that accounts for those peaks.
Storage is another goldmine for optimization. Are you paying a premium for high-performance SSD storage for data that's rarely ever touched? It might be time to move that data to a much more affordable storage tier, like object or archival storage, for a significant cost reduction.
Establishing Strong Governance with a CCoE
As your team starts building more in the cloud, things can get messy fast without some rules of the road. This is where a Cloud Center of Excellence (CCoE) becomes invaluable. Think of a CCoE as a cross-functional team that establishes and enforces best practices for your entire cloud environment.
This team becomes the central authority on:
- Security: Defining baseline security configurations, managing who has access to what, and ensuring you stay compliant with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
- Governance: Setting company-wide standards for how resources are tagged, how new accounts are created, and automating policies to prevent misconfigurations.
- Innovation: Keeping an eye on new cloud services and helping your development teams adopt them in a safe, efficient way.
A CCoE turns cloud usage from a chaotic free-for-all into a governed, secure, and well-oiled machine. It builds a culture of continuous improvement that ensures you get the most out of your cloud investment long after the initial move. To really get a handle on potential costs, it's wise to understand the various service models; exploring different cloud computing pricing structures will give you a much clearer forecast.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cloud Migration
Even with a rock-solid plan, questions are going to pop up. It's just the nature of a big project like moving to the cloud. Over the years, I've heard the same handful of questions from executives, IT managers, and the engineers on the ground. Getting these concerns out in the open and answering them directly can clear up a lot of confusion and get everyone pulling in the same direction.
Here are my honest, practical answers to some of the most common questions I get about cloud migration strategy, cost, and security.
What Is the Most Common Cloud Migration Mistake?
The single biggest mistake I see, and the one that costs the most, is rushing the technical work without doing a proper, thorough assessment first. It happens all the time. Teams get excited about the new tech and dive right in, but skipping that foundational planning almost always comes back to bite them. They don't really know their application dependencies, what their true performance needs are, or the specific business goals they're supposed to be hitting.
This oversight is the root cause of the most common migration headaches:
- Unexpected Downtime: You move an application, only to discover it has a critical, undocumented link to a server still sitting in your old data center. Suddenly, everything grinds to a halt.
- Poor Performance: Without baselining your current environment, you’re just guessing at what kind of cloud resources you need. You might end up with apps that are actually slower than they were before.
- Budget Overruns: Migrating servers you don't actually need or picking a strategy based on bad information is a recipe for a shockingly high cloud bill.
I always tell people to think of it like building a house. You'd never start without a detailed blueprint. Your assessment is that blueprint. It shows you how all your applications talk to each other, where your sensitive data lives, and what security policies are absolute must-haves. Skipping it is the fastest way to a failed project.
How Do I Choose a Cloud Strategy?
Your choice between a single-cloud, multi-cloud, or hybrid approach should have everything to do with your business needs and almost nothing to do with what's trendy. Each one has its own clear advantages and trade-offs.
- Single-Cloud: This is the most straightforward path. Committing to one provider, like AWS or Azure, keeps things simpler to manage. For companies just getting started, it's often the most cost-effective option.
- Multi-Cloud: Here, you’re using services from two or more public clouds. The idea is to pick the "best-of-breed" service for each specific job and avoid getting locked into one vendor. Be warned, though: it adds a ton of complexity and you need a sharp team to manage it well.
- Hybrid Cloud: This approach blends your own private infrastructure with a public cloud. It's the go-to for businesses that have to follow strict data residency laws, meet specific compliance requirements, or have legacy systems with ultra-low latency needs that just can't move.
The right answer always comes from your initial assessment. I've seen a financial services firm with strict data laws lean heavily into a hybrid model, while a fast-growing startup with a skilled team went multi-cloud to cherry-pick the best AI and data tools from different providers.
How Do We Keep Data Secure During Migration?
Security can't be an afterthought—it has to be part of the plan from day one. When you move to the cloud, you're entering a shared responsibility model. The provider secures the cloud itself, but you are 100% responsible for securing what you put in the cloud.
During the migration, the golden rule is to encrypt your data, both in transit and at rest. There's no excuse for not doing this. You have to use secure connections like a VPN or a Direct Connect link for the transfer, and make sure the data is encrypted on both the source and destination storage.
Once you're in the cloud, security becomes a game of constant vigilance. Your focus needs to shift to:
- Strict Access Control: Use a "least privilege" model with solid Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies. This means people and applications only get the permissions they absolutely need to do their jobs, and nothing more.
- Configuration Management: Misconfigurations are a top cause of data breaches. Use a cloud security posture management (CSPM) tool to constantly scan your environment and flag these issues automatically.
- Threat Detection: Set up automated monitoring and alerts. You want to know about suspicious activity the second it happens, not a week later. The faster you know, the faster you can shut it down.
Ultimately, security is as much about culture as it is about technology. Training your team on cloud security best practices is just as crucial as setting up the right firewalls.
Are you preparing your team for the new skills required in a cloud environment? Equip them for success with HydraNode, an AI-driven exam preparation platform that makes mastering certifications from AWS, Microsoft, and Google faster and more effective. Discover how HydraNode can accelerate your team's certification journey.



